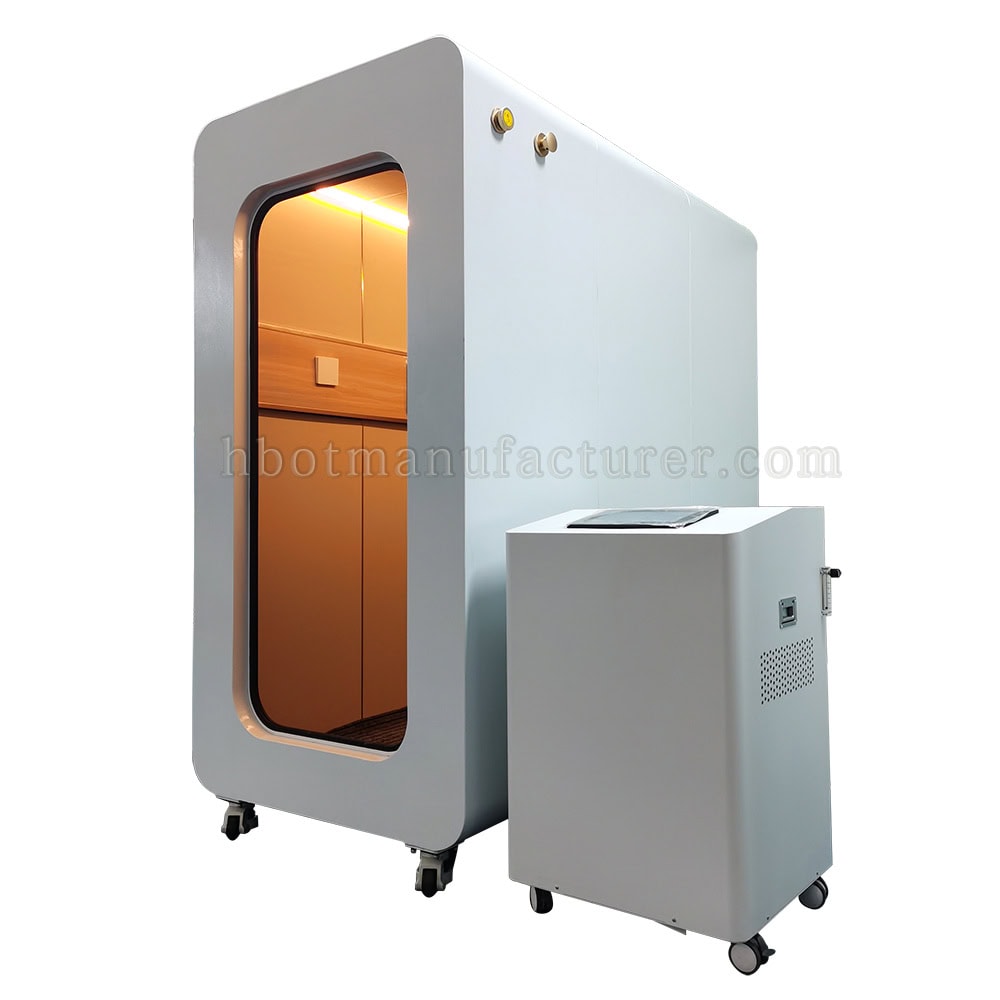
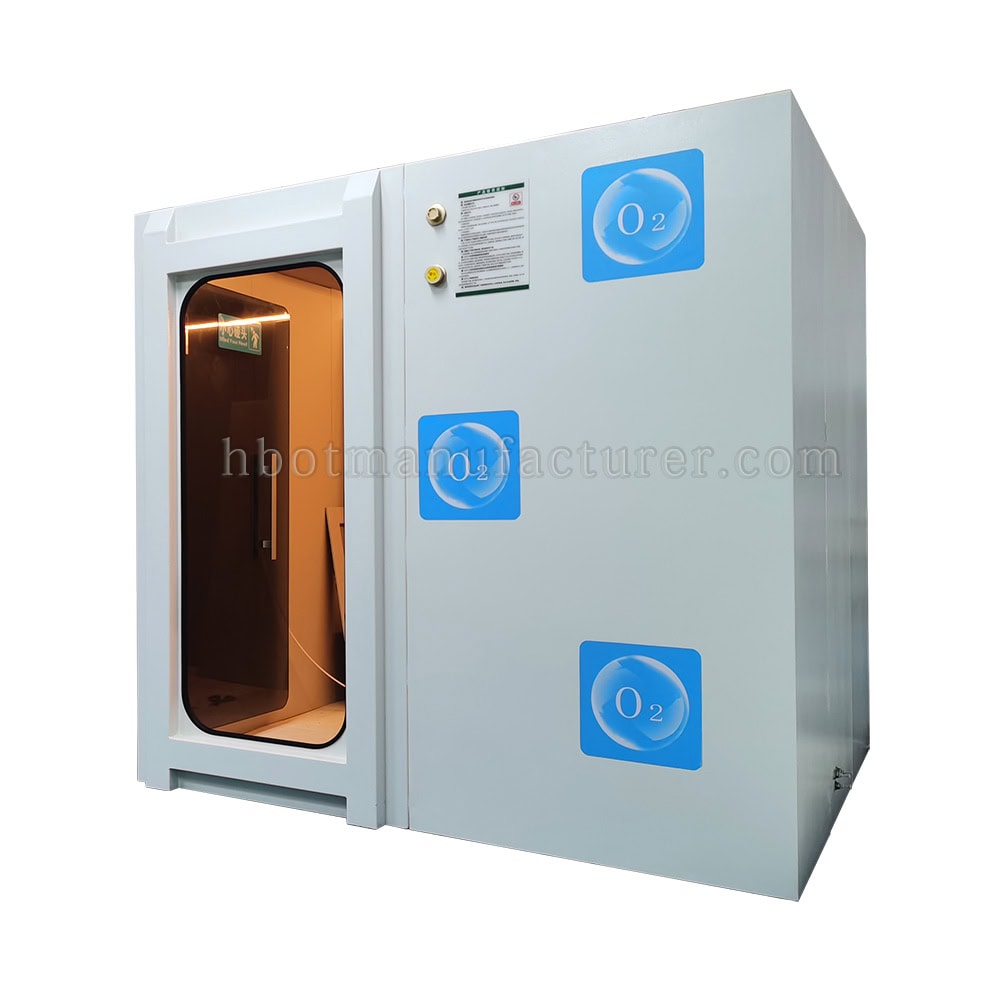
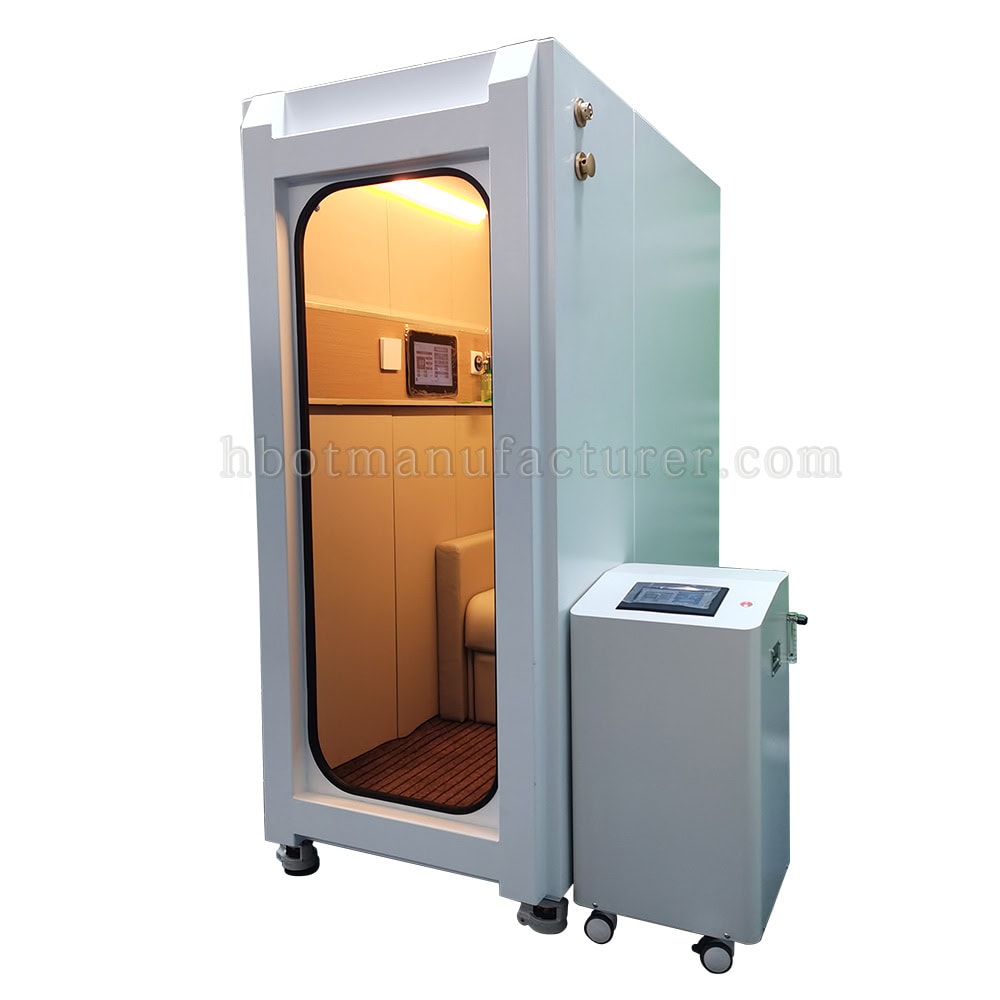
How does a Hyperbaric Chamber Work
Introduction of Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber
A hyperbaric oxygen chamber is filled with pure oxygen, a significant contrast to the normal air we breathe, which contains only about 21% oxygen. This pure oxygen environment is crucial for the effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). The concentrated oxygen levels enable the lungs to absorb more oxygen, enhancing the body’s ability to utilize this essential gas. In a hyperbaric chamber, patients are exposed to 100% oxygen, which is much higher than the atmospheric levels found in everyday air. This enriched oxygen atmosphere supports various physiological processes and is a fundamental aspect of HBOT, contributing to its therapeutic benefits.
Enhanced Oxygen Absorption
The increased air pressure inside the chamber allows your lungs to take in significantly more oxygen than normal. This higher pressure environment forces more oxygen into the bloodstream, surpassing the usual limits of oxygen absorption under standard atmospheric conditions. The elevated pressure ensures that the oxygen dissolves more efficiently into the blood plasma, enhancing its availability to tissues and organs. This process is particularly beneficial for conditions where oxygen supply is compromised, as the enhanced oxygen absorption helps to restore adequate levels in the body, supporting healing and overall health.
Circulation of Oxygen-Rich Blood
This extra oxygen-rich blood is then circulated throughout your body, delivering high concentrations of oxygen to tissues that may be injured or starved of oxygen. The oxygen-enriched blood reaches areas that are typically difficult to oxygenate, such as damaged tissues and cells suffering from hypoxia. By providing these tissues with a surplus of oxygen, HBOT promotes cellular metabolism, supports the repair of damaged structures, and enhances the overall healing process. This comprehensive oxygen delivery is essential for recovering from various medical conditions and improving the body’s resilience against further damage.
Combatting Bacteria and Promoting Healing
The increased oxygen levels help fight bacteria, reduce swelling, and promote the growth of new blood vessels and tissue healing. Oxygen is a critical component of the immune system’s ability to combat infections, particularly anaerobic bacteria that thrive in low-oxygen environments. By elevating the oxygen concentration in tissues, HBOT enhances the body’s natural defenses. Additionally, the therapy reduces inflammation, which can hinder the healing process. The surplus oxygen also stimulates angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, and accelerates the regeneration of tissues, making it a powerful tool for wound healing and recovery.
Prevention of Decompression Sickness
The higher pressure also helps dissolve gases in the blood, preventing the formation of air bubbles that can cause decompression sickness in divers. Decompression sickness, also known as “the bends,” occurs when nitrogen bubbles form in the bloodstream due to rapid pressure changes. The pressurized environment of the hyperbaric chamber helps to dissolve these gases more effectively, ensuring they are safely absorbed and eliminated by the body. This mechanism is crucial for divers who are at risk of developing this condition, providing a reliable treatment option that mitigates the dangers associated with rapid ascents and pressure changes.
Duration and Adjustments During Therapy
Patients typically spend 1-2 hours in the hyperbaric chamber, with the air pressure slowly increased and decreased at the start and end of the session to allow their ears to adjust. The gradual changes in pressure are necessary to prevent discomfort and potential damage to the ears and other air-filled cavities in the body. During a session, patients may relax, read, or sleep while the oxygen therapy takes effect. The controlled environment ensures a safe and effective treatment experience, with healthcare providers monitoring the patient’s response to the therapy to optimize outcomes.
Approved Medical Applications
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been approved to treat a variety of conditions, including serious infections, wounds that won’t heal, carbon monoxide poisoning, and the effects of radiation therapy. The therapy’s ability to enhance oxygen delivery and promote healing makes it a valuable tool in modern medicine. For instance, HBOT is used to treat chronic wounds that are resistant to conventional treatments, providing a much-needed option for patients with diabetic ulcers or other non-healing injuries. It is also effective in managing the aftereffects of radiation therapy, helping to repair damaged tissues and improve quality of life for cancer patients. The broad range of applications highlights the versatility and effectiveness of HBOT in addressing diverse medical challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) stands out as a versatile and potent medical treatment with a wide range of applications. By creating an environment filled with pure oxygen and elevated air pressure, HBOT significantly enhances the body’s ability to absorb and utilize oxygen. This increased oxygen delivery supports various physiological functions, from fighting bacteria and reducing inflammation to promoting wound healing and stimulating the growth of new blood vessels. Moreover, the therapy’s ability to prevent decompression sickness and treat radiation-induced tissue damage showcases its diverse therapeutic benefits. Sessions in the hyperbaric chamber are carefully monitored and adjusted to ensure patient safety and comfort, typically lasting 1-2 hours. Approved for treating serious infections, chronic wounds, carbon monoxide poisoning, and more, HBOT continues to be a valuable tool in modern medicine. Under the supervision of qualified healthcare providers, this advanced therapy offers significant healing potential and improved health outcomes for a variety of medical conditions, making it an indispensable part of contemporary healthcare solutions.